Tensorflow C++ 从训练到部署(3):使用 Keras 训练和部署 CNN
在上一篇文章中我们并没有去训练一个真正的网络和解决一个实际问题,我们所做的是构建了一个 c = a * b 的计算图,并用 python 进行了保存和 c++ 进行了读取,这一保存和读取中也仅包含图的结构并没有相关参数。本篇文章中我们进一步以 Tensorflow 官方的 Fashion MNIST 为例,完成一个简单的分类问题。本文前面 Keras 训练模型以及转化到 Tensorflow 格式部分与之前一篇博客(Keras 转换成 Tensorflow 模型格式并使用)基本一致。本文主要包含:
1)Python:Fashion MNIST 数据集
2)Python:使用 Keras 定义 CNN 模型、训练并保存
3)Python:转换 Keras 模型到 Tensorflow 格式并保存
4)Python:使用 Tensorflow Python API 加载模型并预测
5)C++:使用 Tensorflow C++ API 加载模型并预测
0、系统环境
Ubuntu 16.04
Tensorflow 1.12.0 (安装详见官网,本文环境使用 pip 方式安装)
1、Fashion MNIST 数据集
1)数据简介
Fashion-MNIST [1] 是一个替代MNIST手写数字集的图像数据集。 它是由Zalando(一家德国的时尚科技公司)旗下的研究部门提供。其涵盖了来自10种类别的共7万个不同商品的正面图片。Fashion-MNIST的大小、格式和训练集/测试集划分与原始的MNIST完全一致。60000/10000的训练测试数据划分,28x28的灰度图片。你可以直接用它来测试你的机器学习和深度学习算法性能,且不需要改动任何的代码 [11]。
典型的 Fashion-MNITST 数据是这样的,其中每三行表示一个类别:
![]()
Fashion-MNIST 与 MNIST 同样有 10 个类别,不过并不是 0-9 的 10 个数字,它的类别如下:
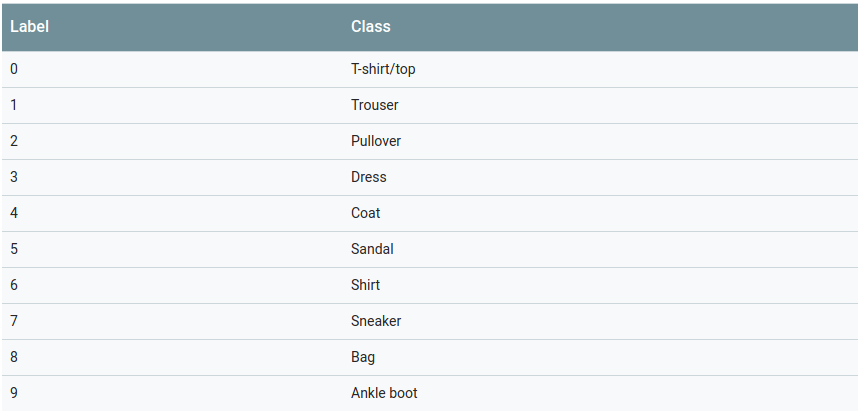
我们使用过以前的 MNIST 数据集都知道,随便弄个很简单的网络,就可以轻轻松松刷出 99% 以上的分数了,即使传统方法也很容易达到高分。所以 MNIST 手写数字识别由于过于简单,作为一个基本的实验数据已经没有什么意义了。Tensorflow 和很多深度学习框架现在的入门数据也都推荐 Fashion MNIST。
2)数据读取
其实 Keras 为我们提供了简单的接口可以一键下载 Fashion-MNIST 数据并且读取:
1 2 | from keras.datasets import fashion_mnist (x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = fashion_mnist.load_data() |
不过由于天朝网络的原因,我并不推荐这种方式,建议直接下载到本地读取。我这里将数据直接存到 data/fashion 目录下。
百度网盘下载:
https://pan.baidu.com/s/19zZqU5tSwZyY780z8Y8_VA
读取数据代码如下(保存为:utils/mnist_reader.py):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | def load_mnist(path, kind='train'): import os import gzip import numpy as np """Load MNIST data from `path`""" labels_path = os.path.join(path, '%s-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz' % kind) images_path = os.path.join(path, '%s-images-idx3-ubyte.gz' % kind) with gzip.open(labels_path, 'rb') as lbpath: labels = np.frombuffer(lbpath.read(), dtype=np.uint8, offset=8) with gzip.open(images_path, 'rb') as imgpath: images = np.frombuffer(imgpath.read(), dtype=np.uint8, offset=16).reshape(len(labels), 784) return images, labels |
2、使用 Keras 定义 CNN 模型、训练并保存
下面的代码中我们定义了一个非常简单的 CNN 网络,结构图如下:
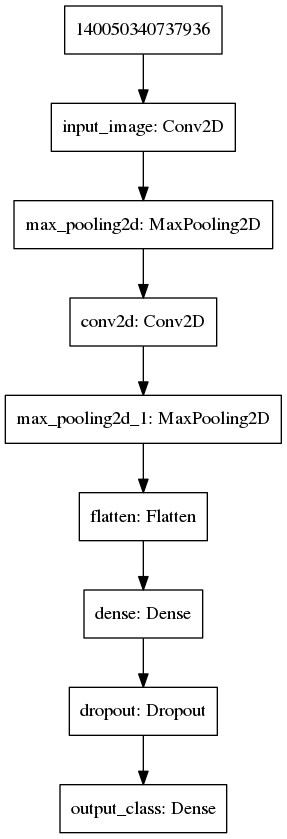
我们使用这一网络进行训练并且保存为 Keras 标准的 h5 格式。这一部分代码比较基础,就不做过多解释了。
Keras 模型定义和训练代码如下(保存为:train.py):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 | # TensorFlow and tf.keras import os import gzip import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow import keras from tensorflow.keras import Sequential from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Dropout, Flatten from tensorflow.keras.layers import Conv2D, MaxPooling2D from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import SGD from tensorflow.keras import backend as K # Use this only for export of the model. K.set_learning_phase(0) K.set_image_data_format('channels_last') sess = K.get_session() # Helper libraries import numpy as np # Plot model from tensorflow.keras.utils import plot_model # Dataset import utils.mnist_reader as mnist_reader # Model from model import create_model print(tf.__version__) print(keras.__version__) train_images, train_labels = mnist_reader.load_mnist('data/fashion', kind='train') test_images, test_labels = mnist_reader.load_mnist('data/fashion', kind='t10k') class_names = ['T-shirt/top', 'Trouser', 'Pullover', 'Dress', 'Coat', 'Sandal', 'Shirt', 'Sneaker', 'Bag', 'Ankle boot'] train_images = train_images.reshape(train_images.shape[0], 28, 28, 1) test_images = test_images.reshape(test_images.shape[0], 28, 28, 1) train_images = train_images.astype('float32') test_images = test_images.astype('float32') train_images /= 255 test_images /= 255 # convert class vectors to binary class matrices train_labels = tf.keras.utils.to_categorical(train_labels, 10) test_labels = tf.keras.utils.to_categorical(test_labels, 10) # Create CNN Model from model.py model = create_model() # Take a look at the model summary model.summary() # Virtualize model from tensorflow.keras.utils import plot_model plot_model(model, to_file='model.png') # Include the epoch in the file name. (uses `str.format`) checkpoint_path="train_logs/cp-{epoch:04d}.hdf5" cp_callback = tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint( checkpoint_path, verbose=1, save_weights_only=False, # Save weights, every 5-epochs. period=5) # Comile model with loss and optimizer model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy']) # Train model model.fit(train_images, train_labels, batch_size=64, callbacks = [cp_callback], epochs=10) model.evaluate(test_images, test_labels) # Evaluate the model on test set score = model.evaluate(test_images, test_labels, verbose=0) print("%s: %.2f%%" % (model.metrics_names[1], score[1]*100)) # Predict using Keras predictions = model.predict(test_images) pred_index = np.argmax(predictions[0]) # Print test accuracy print('Predict:', pred_index, ' Label:', class_names[pred_index], 'GT:', test_labels[0]) # Save whole graph & weights model_path = "models/fashion_mnist.h5" model.save(model_path) print('Finish writing model to : {}'.format(model_path)) print('You can convert model to tensorflow format:\npython3 utils/keras_to_tensorflow.py -input_model_file {} -output_model_file {}'.format(model_path, model_path + ".pb")) |
如果你的运行没有问题则会看到类似如下输出:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | Epoch 00010: saving model to train_logs/cp-0010.hdf5 10000/10000 [==============================] - 0s 44us/step acc: 91.95% Predict: 9 Label: Ankle boot GT: [0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1.] Finish writing model to : models/fashion_mnist.h5 You can convert model to tensorflow format: python3 utils/keras_to_tensorflow.py -input_model_file models/fashion_mnist.h5 -output_model_file models/fashion_mnist.h5.pb |
同时在 models/ 文件夹下保存了 fashion_mnist.h5 文件,这一文件包含了模型的结构和参数。
3、转换 Keras 模型到 Tensorflow 格式并保存
这一环节我们使用 keras_to_tensorflow [2] 转换工具进行模型转换,其实这个工具原理很简单,首先用 Keras 读取 .h5 模型文件,然后用 tensorflow 的 convert_variables_to_constants 函数将所有变量转换成常量,最后再 write_graph 就是一个包含了网络以及参数值的 .pb 文件了。
具体代码参见(原始代码中可以传入输出 node 数量和名字并使用 identity 生成新的 tensor,我这里稍作修改,直接读取 Keras 的 outputs 的操作名,最后会输出原始 inputs 和 outputs 的名字供后面使用):
Tensorflow 模型转换代码(保存为:utils/keras_to_tensorflow.py)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 | # coding: utf-8 # In[ ]: """ Copyright (c) 2017, by the Authors: Amir H. Abdi This software is freely available under the MIT Public License. Please see the License file in the root for details. The following code snippet will convert the keras model file, which is saved using model.save('kerasmodel_weight_file'), to the freezed .pb tensorflow weight file which holds both the network architecture and its associated weights. """; # In[ ]: ''' Input arguments: num_output: this value has nothing to do with the number of classes, batch_size, etc., and it is mostly equal to 1. If the network is a **multi-stream network** (forked network with multiple outputs), set the value to the number of outputs. quantize: if set to True, use the quantize feature of Tensorflow (https://www.tensorflow.org/performance/quantization) [default: False] use_theano: Thaeno and Tensorflow implement convolution in different ways. When using Keras with Theano backend, the order is set to 'channels_first'. This feature is not fully tested, and doesn't work with quantizization [default: False] input_fld: directory holding the keras weights file [default: .] output_fld: destination directory to save the tensorflow files [default: .] input_model_file: name of the input weight file [default: 'model.h5'] output_model_file: name of the output weight file [default: args.input_model_file + '.pb'] graph_def: if set to True, will write the graph definition as an ascii file [default: False] output_graphdef_file: if graph_def is set to True, the file name of the graph definition [default: model.ascii] output_node_prefix: the prefix to use for output nodes. [default: output_node] ''' # Parse input arguments # In[ ]: import argparse parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='set input arguments') parser.add_argument('-input_fld', action="store", dest='input_fld', type=str, default='.') parser.add_argument('-output_fld', action="store", dest='output_fld', type=str, default='') parser.add_argument('-input_model_file', action="store", dest='input_model_file', type=str, default='model.h5') parser.add_argument('-output_model_file', action="store", dest='output_model_file', type=str, default='') parser.add_argument('-output_graphdef_file', action="store", dest='output_graphdef_file', type=str, default='model.ascii') parser.add_argument('-num_outputs', action="store", dest='num_outputs', type=int, default=1) parser.add_argument('-graph_def', action="store", dest='graph_def', type=bool, default=False) parser.add_argument('-output_node_prefix', action="store", dest='output_node_prefix', type=str, default='output_node') parser.add_argument('-quantize', action="store", dest='quantize', type=bool, default=False) parser.add_argument('-theano_backend', action="store", dest='theano_backend', type=bool, default=False) parser.add_argument('-f') args = parser.parse_args() parser.print_help() print('input args: ', args) if args.theano_backend is True and args.quantize is True: raise ValueError("Quantize feature does not work with theano backend.") # initialize # In[ ]: import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.keras.models import load_model from pathlib import Path from tensorflow.keras import backend as K output_fld = args.input_fld if args.output_fld == '' else args.output_fld if args.output_model_file == '': args.output_model_file = str(Path(args.input_model_file).name) + '.pb' Path(output_fld).mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True) weight_file_path = str(Path(args.input_fld) / args.input_model_file) # Load keras model and rename output # In[ ]: K.set_learning_phase(0) if args.theano_backend: K.set_image_data_format('channels_first') else: K.set_image_data_format('channels_last') try: net_model = load_model(weight_file_path) except ValueError as err: print('''Input file specified ({}) only holds the weights, and not the model defenition. Save the model using mode.save(filename.h5) which will contain the network architecture as well as its weights. If the model is saved using model.save_weights(filename.h5), the model architecture is expected to be saved separately in a json format and loaded prior to loading the weights. Check the keras documentation for more details (https://keras.io/getting-started/faq/)''' .format(weight_file_path)) raise err # num_output = args.num_outputs # pred = [None]*num_output # pred_node_names = [None]*num_output # for i in range(num_output): # pred_node_names[i] = args.output_node_prefix+str(i) # pred[i] = tf.identity(net_model.outputs[i], name=pred_node_names[i]) # num_output = len(net_model.output_names) # pred_node_names = [None]*num_output # pred = [None]*num_output # # pred_node_names = net_model.output_names # for i in range(num_output): # pred_node_names[i] = args.output_node_prefix+str(i) # pred[i] = tf.identity(net_model.outputs[i], name=pred_node_names[i]) input_node_names = [node.op.name for node in net_model.inputs] print('Input nodes names are: ', input_node_names) pred_node_names = [node.op.name for node in net_model.outputs] print('Output nodes names are: ', pred_node_names) # print("net_model.input.op.name:", net_model.input.op.name) # print("net_model.output.op.name:", net_model.output.op.name) # print("net_model.input_names:", net_model.input_names) # print("net_model.output_names:", net_model.output_names) # [optional] write graph definition in ascii # In[ ]: sess = K.get_session() if args.graph_def: f = args.output_graphdef_file tf.train.write_graph(sess.graph.as_graph_def(), output_fld, f, as_text=True) print('saved the graph definition in ascii format at: ', str(Path(output_fld) / f)) # convert variables to constants and save # In[ ]: from tensorflow.python.framework import graph_util from tensorflow.python.framework import graph_io if args.quantize: from tensorflow.tools.graph_transforms import TransformGraph transforms = ["quantize_weights", "quantize_nodes"] transformed_graph_def = TransformGraph(sess.graph.as_graph_def(), [], pred_node_names, transforms) constant_graph = graph_util.convert_variables_to_constants(sess, transformed_graph_def, pred_node_names) else: constant_graph = graph_util.convert_variables_to_constants(sess, sess.graph.as_graph_def(), pred_node_names) graph_io.write_graph(constant_graph, output_fld, args.output_model_file, as_text=False) print('saved the freezed graph (ready for inference) at: ', str(Path(output_fld) / args.output_model_file)) |
我们执行如下命令转换 Keras 模型到 Tensorflow 的 pb 格式:
1 | python3 utils/keras_to_tensorflow.py -input_model_file models/fashion_mnist.h5 -output_model_file models/fashion_mnist.h5.pb |
如果你的运行无误的话则会显示如下信息并生成 models/fashion_mnist.h5.pb 这个就是转换过来的 Tensorflow 格式:
1 2 3 | Input nodes names are: ['input_image_input'] Output nodes names are: ['output_class/Softmax'] saved the freezed graph (ready for inference) at: models/fashion_mnist.h5.pb |
这里面也告知了你模型输入和输出的 Tensor 名字,这两个信息很重要我们后面会用到。
4、使用 Tensorflow Python API 加载模型并预测
我们使用标准的 Tensorflow Low-Level API 加载和预测代码如下(保存为:load_predict.py)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 | #!/usr/bin/env python import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np from tensorflow.python.platform import gfile # OpenCV import cv2 class_names = ['T-shirt/top', 'Trouser', 'Pullover', 'Dress', 'Coat', 'Sandal', 'Shirt', 'Sneaker', 'Bag', 'Ankle boot'] # Read image img = cv2.imread('fashion_0.png', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE) print('img.shape = ', img.shape) img = img.astype('float32') img /= 255.0 img = img.reshape(1, 28, 28, 1) # Initialize a tensorflow session with tf.Session() as sess: # Load the protobuf graph with gfile.FastGFile("models/fashion_mnist.h5.pb",'rb') as f: graph_def = tf.GraphDef() graph_def.ParseFromString(f.read()) # Add the graph to the session tf.import_graph_def(graph_def, name='') # Get graph graph = tf.get_default_graph() # Get tensor from graph pred = graph.get_tensor_by_name("output_class/Softmax:0") # Run the session, evaluating our "c" operation from the graph res = sess.run(pred, feed_dict={'input_image_input:0': img}) # Print test accuracy pred_index = np.argmax(res[0]) # Print test accuracy print('Predict:', pred_index, ' Label:', class_names[pred_index]) |
这段代码中前面同样是读取 Fashion MNIST 数据集,与训练代码一样。部分代码说明如下:
读取 pb 模型文件:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | # Load the protobuf graph with gfile.FastGFile("models/fashion_mnist.h5.pb",'rb') as f: graph_def = tf.GraphDef() graph_def.ParseFromString(f.read()) # Add the graph to the session tf.import_graph_def(graph_def, name='') |
获取当前的计算图:
1 2 | # Get graph graph = tf.get_default_graph() |
获取输出的 Tensor:
1 2 | # Get tensor from graph pred = graph.get_tensor_by_name("output_class/Softmax:0") |
可以看到除了之前我们给出的输出 Tensor 名称 output_class/Softmax 外,我们还需要加上一个索引 :0。关于这一问题的解释可以参见 [12]。我们这里简单来理解,"output_class/Softmax" 是指定了一个 Operation 的名字,对应最后 Softmax 层,大部分层的输出都是一个 Tensor,不过也有可能一个层产生多个输出 Tensor,因此我们这里需要指定是哪个输出。通常对于一个输出的时候就是用 :0 指定,对于 Input 也是同理。
执行计算图并打印输出结果,其中 feed_dict={'input_image_input:0': test_images} 将 test_images 作为输入传入网络:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | # Run the session, evaluating our "c" operation from the graph res = sess.run(pred, feed_dict={'input_image_input:0': test_images}) # Print test accuracy pred_index = np.argmax(res[0]) # Print test accuracy print('Predict:', pred_index, ' Label:', class_names[pred_index], 'GT:', test_labels[0]) |
执行整个代码:
1 | python3 load_predict.py |
如果运行没有问题则可以看到如下结果:
1 | Predict: 9 Label: Ankle boot GT: 9 |
与之前我们使用 Keras 的 predict 接口结果对比,是一样的,说明我们转换后的模型无误。
关于 Keras 转换成 Tensorflow 模型和预测的步骤就到这里。完整示例可以参见:
https://github.com/skylook/tensorflow_cpp
5、使用 Tensorflow C++ API 加载模型并预测
1)使用 C++ 转换 OpenCV 的 Mat 到 Tensor
Tensor 要求输入的是归一化的 float32 格式图片,实际我们使用如下代码来完成 OpenCV Mat 到 Tensor 的转换(保存为:utils/mat2tensor.h)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 | // // Created by skylook on 18-10-12. // #ifndef TENSORFLOW_CPP_IMG2TENSOR_H #define TENSORFLOW_CPP_IMG2TENSOR_H #include "tensorflow/cc/ops/const_op.h" #include "tensorflow/cc/ops/image_ops.h" #include "tensorflow/cc/ops/standard_ops.h" #include "tensorflow/core/framework/graph.pb.h" #include "tensorflow/core/framework/tensor.h" #include "tensorflow/core/graph/default_device.h" #include "tensorflow/core/graph/graph_def_builder.h" #include "tensorflow/core/lib/core/errors.h" #include "tensorflow/core/lib/core/stringpiece.h" #include "tensorflow/core/lib/core/threadpool.h" #include "tensorflow/core/lib/io/path.h" #include "tensorflow/core/lib/strings/stringprintf.h" #include "tensorflow/core/platform/env.h" #include "tensorflow/core/platform/init_main.h" #include "tensorflow/core/platform/logging.h" #include "tensorflow/core/platform/types.h" #include "tensorflow/core/public/session.h" #include "tensorflow/core/util/command_line_flags.h" //#include "TensorflowObjectDetection.h" #include <utility> #include <fstream> #include <regex> #include <iostream> #include <utility> #include <vector> #include "opencv2/core/core.hpp" tensorflow::Tensor Mat2Tensor(cv::Mat &img, float normal = 1/255.0) { tensorflow::Tensor image_input = tensorflow::Tensor(tensorflow::DT_FLOAT, tensorflow::TensorShape( {1, img.size().height, img.size().width, img.channels()})); float *tensor_data_ptr = image_input.flat<float>().data(); cv::Mat fake_mat(img.rows, img.cols, CV_32FC(img.channels()), tensor_data_ptr); img.convertTo(fake_mat, CV_32FC(img.channels())); fake_mat *= normal; return image_input; } #endif //TENSORFLOW_CPP_IMG2TENSOR_H |
这段代码比较简单,就是声明一个 {1, img.size().height, img.size().width, img.channels()} 的单个 Tensor,将地址直接赋给 fake_mat,然后使用 OpenCV 把图片转成 float32 格式,声明的 Tensor 自然也就转成了 float32 格式。最后是根据输入 normal 因子进行归一化。这一归一化方法和之前训练时一致。
2)使用 C++ 调用 pb 模型并预测
与前面的文章类似,我们参考 Python 调用 pb 模型及预测接口使用 C++ API 调用之前转换的模型并预测代码如下(保存为:load_predict.cpp):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 | // // Created by skylook on 18-9-19. // #include "utils/mat2tensor.h" #include "tensorflow/core/public/session.h" #include "tensorflow/core/platform/env.h" // OpenCV #include <opencv2/core/core.hpp> #include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp> using namespace tensorflow; //std::string class_names[10] = {'T-shirt/top', 'Trouser', 'Pullover', 'Dress', 'Coat', 'Sandal', 'Shirt', 'Sneaker', 'Bag', 'Ankle boot'}; std::string class_names[] = {"T-shirt/top", "Trouser", "Pullover", "Dress", "Coat", "Sandal", "Shirt", "Sneaker", "Bag", "Ankle boot"}; int ArgMax(const tensorflow::TTypes<float, 1>::Tensor& prediction); /** * @brief simple model for click through rate prediction * @details [long description] * * @param argv[1] graph protobuf * * @return [description] */ int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { // Initialize a tensorflow session Session* session; Status status = NewSession(SessionOptions(), &session); if (!status.ok()) { std::cerr << status.ToString() << std::endl; return 1; } else { std::cout << "Session created successfully" << std::endl; } if (argc != 3) { std::cerr << std::endl << "Usage: ./project path_to_graph.pb path_to_image.png" << std::endl; return 1; } // Load the protobuf graph GraphDef graph_def; std::string graph_path = argv[1]; status = ReadBinaryProto(Env::Default(), graph_path, &graph_def); if (!status.ok()) { std::cerr << status.ToString() << std::endl; return 1; } else { std::cout << "Load graph protobuf successfully" << std::endl; } std::string image_path = argv[2]; cv::Mat image = cv::imread(image_path, CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE); Tensor input_image = Mat2Tensor(image, 1/255.0); // Add the graph to the session status = session->Create(graph_def); if (!status.ok()) { std::cerr << status.ToString() << std::endl; return 1; } else { std::cout << "Add graph to session successfully" << std::endl; } // Setup inputs and outputs: std::vector<std::pair<string, tensorflow::Tensor>> inputs = { { "input_image_input:0", input_image } }; // The session will initialize the outputs std::vector<tensorflow::Tensor> outputs; // Run the session, evaluating our "c" operation from the graph status = session->Run(inputs, {"output_class/Softmax:0"}, {}, &outputs); if (!status.ok()) { std::cerr << status.ToString() << std::endl; return 1; } else { std::cout << "Run session successfully" << std::endl; } // Grab the first output (we only evaluated one graph node: "c") // and convert the node to a scalar representation. // Print the results std::cout << outputs[0].DebugString() << std::endl; // Tensor<type: float shape: [] values: 30> // const Eigen::TensorMap<Eigen::Tensor<float, 1, Eigen::RowMajor>, Eigen::Aligned>& prediction = outputs[0].flat<float>(); const tensorflow::TTypes<float, 1>::Tensor& prediction = outputs[0].flat_inner_dims<float, 1>(); int pred_index = ArgMax(prediction); // Print test accuracy printf("Predict: %d Label: %s", pred_index, class_names[pred_index].c_str()); // Free any resources used by the session session->Close(); return 0; } int ArgMax(const tensorflow::TTypes<float, 1>::Tensor& prediction) { float max_value = -1.0; int max_index = -1; const long count = prediction.size(); for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) { const float value = prediction(i); if (value > max_value) { max_index = i; max_value = value; } std::cout << "value[" << i << "] = " << value << std::endl; } return max_index; } |
如果编译运行没有问题的话,会输出如下结果:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | Session created successfully Load graph protobuf successfully Add graph to session successfully Run session successfully Tensor<type: float shape: [1,10] values: [2.21357173e-08 1.92015683e-08 1.26053363e-08]...> value[0] = 2.21357e-08 value[1] = 1.92016e-08 value[2] = 1.26053e-08 value[3] = 6.9663e-09 value[4] = 1.11407e-09 value[5] = 0.000217644 value[6] = 1.12208e-09 value[7] = 0.000137897 value[8] = 5.38564e-07 value[9] = 0.999644 Predict: 9 Label: Ankle boot |
输入和调用模型与之前的博客基本一致,这里解释下输出部分:
1 | const tensorflow::TTypes<float, 1>::Tensor& prediction = outputs[0].flat_inner_dims<float, 1>(); |
这里 flat_inner_dims 的 API 官方说明如下:

表示将按照指定类型 T 和指定维度 NDIMS 的 Eigen::TensorMap 输出,需要说明的是这一 T 和 NDMS 维度必须与模型中实际输出类型一致,否则运行时会报错。TensorMap 相当于 Tensor 的一个引用,其内存地址并不像 Tensor 一样是自己创建与释放的,因此没有 resize 等操作,其他使用方法与 Tensor 类似。关于 Eigen::Tensor 使用说明参见 [6] 和 [7]。
其中 tensorflow::TTypes
1 | const Eigen::TensorMap<Eigen::Tensor<float, 1, Eigen::RowMajor>, Eigen::Aligned>& prediction = outputs[0].flat<float>(); |
到这里我们就完整介绍了一个 CNN 网络从 Keras 训练、转成 Tensorflow 格式到 C++ 部署的基本流程。
本文完整代码参见 Github:
https://github.com/skylook/tensorflow_cpp
参考文献
[1] https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/keras/basic_classification
[2] https://medium.com/tensorflow/hello-deep-learning-fashion-mnist-with-keras-50fcff8cd74a
[3] https://github.com/zalandoresearch/fashion-mnist
[4] https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/30985013
[5] https://github.com/ADozois/proc_deep_detector
[6] http://eigen.tuxfamily.org/index.php?title=Tensor_support
[7] https://github.com/PX4/eigen/blob/master/unsupported/Eigen/CXX11/src/Tensor/README.md
[8] https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/cc/class/tensorflow/tensor
Tensorflow C++ 从训练到部署系列文章目录
| Tensorflow C++ 从训练到部署(3):使用 Keras 训练和部署 CNN |
| Tensorflow C++ 从训练到部署(2):简单图的保存、读取与 CMake 编译 |
| Tensorflow C++ 从训练到部署(1):环境搭建 |